Figure. Flowchart to guide which infants should receive nirsevimab in their 1st RSV season
Figure. Flowchart to guide which infants should receive nirsevimab in their 1st RSV season
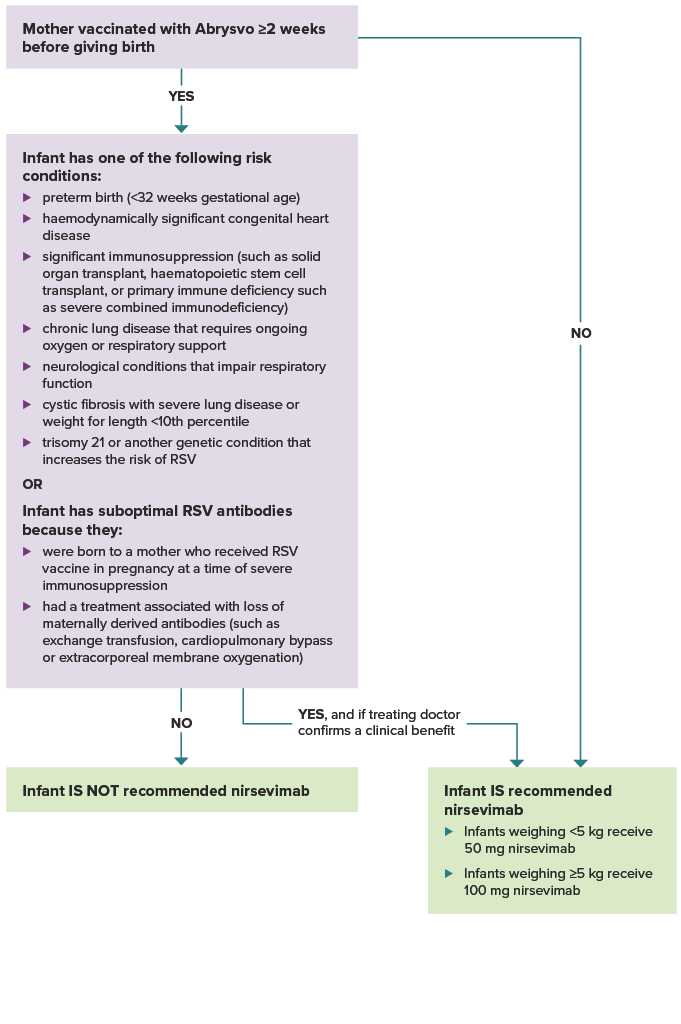
Was the mother vaccinated with Abrysvo at least 2 weeks before giving birth? If yes, and the infant does not have one of the risk conditions or conditions for suboptimal antibodies listed below, the infant is not recommended nirsevimab.
If the mother was not vaccinated at least 2 weeks before delivery, the infant is recommended nirsevimab. Infants weighing less than 5 kg receive 50 mg nirsevimab. Infants weighing 5 kg or more receive 100 mg nirsevimab.
If the mother was vaccinated at least 2 weeks before delivery, does the infant have one of the following risk conditions: preterm birth (<32 weeks gestational age), haemodynamically significant congenital heart disease. significant immunosuppression (such as from malignancy, solid organ transplant, haematopoietic stem cell transplant, or primary immune deficiency such as severe combined immunodeficiency), chronic lung disease that requires ongoing oxygen or respiratory support, neurological conditions that impair respiratory function, cystic fibrosis with severe lung disease or weight for length <10th percentile, trisomy 21 or another genetic condition that increases the risk of RSV? Or, does the infant have suboptimal RSV antibodies because they were born to a mother who received RSV vaccine in pregnancy at a time of severe immunosuppression, or they had a treatment associated with loss of maternally derived antibodies (such as exchange transfusion, cardiopulmonary bypass or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation)? If the infant does not have a risk condition or suboptimal RSV antibodies, they are not recommended nirsevimab. If the infant does have a risk condition or suboptimal RSV antibodies, they are recommended nirsevimab if their treating doctor confirms a clinical benefit.
These files may not be suitable for users of assistive technology.

