Figure. Rabies post-exposure prophylaxis: terrestrial animal exposures
This algorithm gives guidance on post-exposure prophylaxis after potential exposure to lyssaviruses from a terrestrial animal in a rabies-enzootic area.
Figure. Rabies post-exposure prophylaxis: terrestrial animal exposures
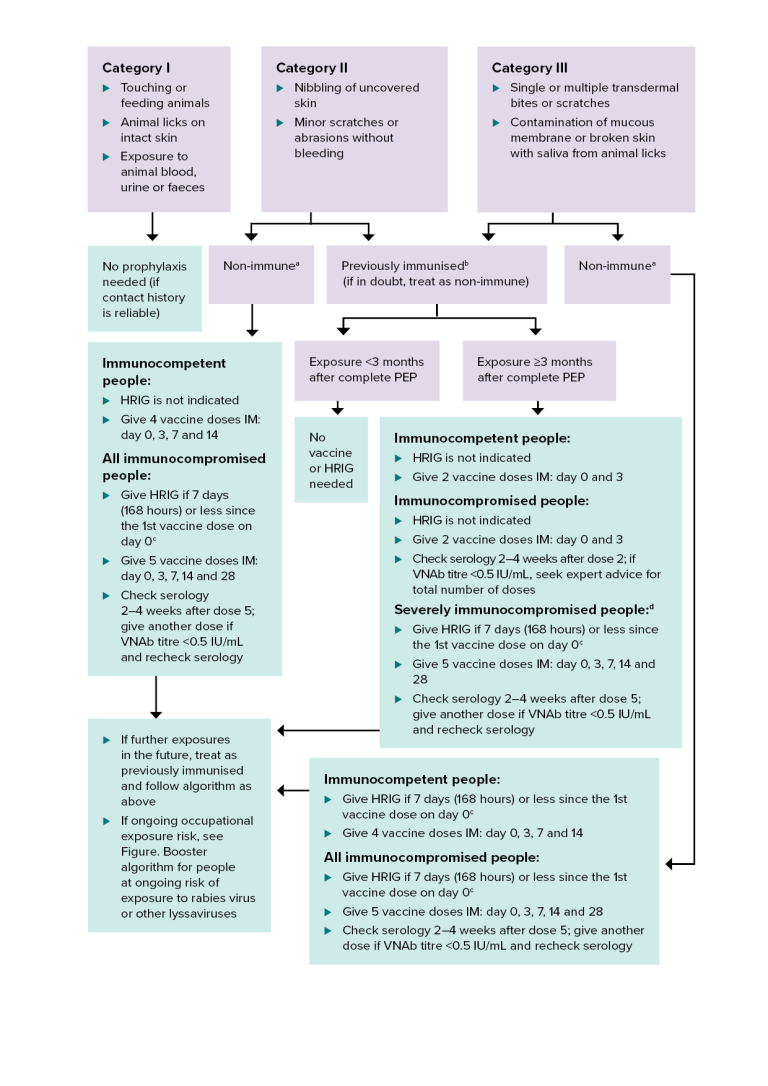
HRIG = human rabies immunoglobulin; IM = intramuscularly; IU = international units; PEP = post-exposure prophylaxis; VNAb = virus neutralising antibody
a Non-immune — person who has never received pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis with rabies vaccine, or has had an incomplete (<2 doses) primary vaccination course.
b Previously immunised — documentation of at least 2 doses of pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis rabies vaccine, regardless of the time since the last dose was given. It may be either a completed primary pre-exposure course or a post-exposure course. It includes people who had subsequent boosters, or who have documented rabies VNAb titres ≥0.5 IU/mL. For more details, see Incomplete pre-exposure prophylaxis schedule.
c Give HRIG in a different limb to the vaccine.
d For defining the level of immunocompromise, see Definitions and Table. Types of medical conditions and immunosuppressive therapy and associated levels of immunocompromise in Vaccination for people who are immunocompromised.
This algorithm gives guidance on post-exposure prophylaxis after potential exposure to lyssaviruses from a terrestrial animal in a rabies-enzootic area.
There are 3 categories of rabies exposure:
- Category 1. Touching or feeding animals, animal licks on intact skin, or exposure to animal blood, urine or faeces.
- Category 2. Animal nibbling of uncovered skin, or minor scratches or abrasions without bleeding.
- Category 3. Single or multiple transdermal bites or scratches; contamination of mucous membrane or broken skin with saliva from animal licks.
Category 1 exposure does not require any prophylaxis if the contact history is reliable.
Category 2 exposure in a non-immune person (see note a). For immunocompetent people, HRIG is not indicated; give 4 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7 and 14. For all immunocompromised people with a category 2 exposure, give HRIG if 7 days (168 hours) or less since the 1st vaccine dose on day 0 (see note c); give 5 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7, 14 and 28; check serology 2–4 weeks after dose 5; give another dose if VNAb titre is <0.5 IU/mL and recheck serology.
Category 2 or 3 exposure in a person who has been previously immunised (see note b; if in doubt, treat as non-immune). If exposure is <3 months after complete post-exposure prophylaxis, no vaccine or HRIG is needed. If exposure is 3 months or longer after complete post-exposure prophylaxis, vaccination is required. For immunocompetent people, HRIG is not indicated; give 2 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0 and 3. For immunocompromised people, HRIG is not indicated; give 2 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0 and 3; check serology 2–4 weeks after dose 2; if VNAb titre is <0.5 IU/mL, seek expert advice for total number of doses. For severely immunocompromised people (see note d), give HRIG if 7 days (168 hours) or less since the 1st vaccine dose on day 0 (see note c); give 5 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7, 14 and 28; check serology 2–4 weeks after dose 5; give another dose if VNAb titre is <0.5 IU/mL and recheck serology.
Category 3 exposure in a non-immune person (see note a). For immunocompetent people, give HRIG if 7 days (168 hours) or less since the 1st vaccine dose on day 0 (see note c); give 4 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7 and 14. For all immunocompromised people, give HRIG if 7 days (168 hours) or less since the 1st vaccine dose on day 0 (see note c); give 5 vaccine doses intramuscularly on days 0, 3, 7, 14 and 28; check serology 2–4 weeks after dose 5; give another dose if VNAb titre is <0.5 IU/mL and recheck serology.
For all exposure groups, if there are further exposures in the future, treat as previously immunised and follow the algorithm as above. If there is ongoing occupational exposure risk, see Figure. Booster algorithm for people at ongoing risk of exposure to rabies virus or other lyssaviruses.
These files may not be suitable for users of assistive technology.

